
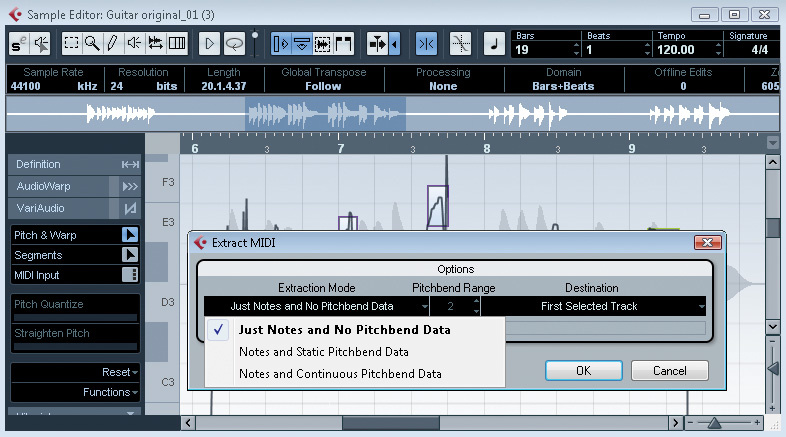
While this suite does provide some functionality accessible only if you're comfortable with various kinds of references, and while there are some options that deal with the guts of MIDI encoding, you can (I hope) get along just fine with just a basic grasp of the MIDI "standard", and a command of LoLs.
This is the level of abstraction that MIDI::Score and MIDI::Simple deal with. In other words, opuses and tracks are objects, and the events in a track comprise a LoL (and if you don't know what an LoL is, you must read perllol).įurthermore, for some purposes it's useful to analyze the totality of a track's events as a "score" - where a score consists of notes where each event is a list consisting of a command, a time offset from the start of the track, and some number of parameters. A track will generally contain a list of events, where each event is a list consisting of a command, a delta-time, and some number of parameters.

An opus contains tracks, which are objects belonging to the class MIDI::Track. MIDI opuses ("songs") are represented as objects belonging to the class MIDI::Opus. This suite of modules is basically object-oriented, with the exception of MIDI::Simple. The order you want to read them in will depend on what you want to do with this suite of modules: if you are focused on manipulating the guts of existing MIDI files, read the pods in the order given above.īut if you aim to compose music with this suite, read this pod, then MIDI::Score and MIDI::Simple, and then skim the rest. All of these contain documentation in pod format. MIDI (which you're looking at), MIDI::Opus, MIDI::Track, MIDI::Event, MIDI::Score, and MIDI::Simple. The MIDI-Perl suite consists of these modules: There is a file format for expressing MIDI data which is like a dump of data sent over a MIDI port. There are many other message types for events such as pitch bend, patch changes and synthesizer-specific events for loading new patches etc. The basic unit of information is a "note on/off" event which includes a note number (pitch) and key velocity (loudness). (MIDI /mi'-dee/, /mee'-dee/) A hardware specification and protocol used to communicate note and effect information between synthesisers, computers, music keyboards, controllers and other electronic music devices. MIDI, Musical Instrument Digital Interface

This suite of modules provides routines for reading, composing, modifying, and writing MIDI files. $opus->write_to_file( 'cowbell.mid' ) DESCRIPTION MIDI - read, compose, modify, and write MIDI files SYNOPSIS use MIDI


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
